There are two types of web crawling strategies deployed by web search engines, viz., breadth first search strategy and ``best'' first search strategy. Breadth first search strategy endeavors to build a general index of the web covering any conceivable topic by endeavoring to search a significant portion of the web. The ``best'' first search focuses on the retrieval of pages which are relevant to a particular given topic. A crawler using a ``best'' first search strategy is known as a ``focused crawler''.
A focused crawler has the following main components: (a) A way to determine if a particular web page is relevant to the given topic, and (b) a way to determine how to proceed from a known set of pages. An early search engine which deployed the focused crawling strategy was proposed in [1] based on the intuition that relevant pages often contain relevant links. It searches deeper when relevant pages are found, and stops searching at pages not as relevant to the topic. Unfortunately, the above crawlers show an important drawback when the pages about a topic are not directly connected in which case the crawling might stop pre-maturely.
This problem is tackled in [3] where reinforcement learning permits credit assignment during the search process, and hence, allowing off-topic pages to be included in the search path. However, this approach requires a large number of training examples, and the method can only be trained offline. In [2], a set of classifiers are trained on examples to estimate the distance of the current page from the closest on-topic page. But the training procedure is quite complex.
Our focused crawler aims at providing a simpler alternative for
overcoming the issue that immediate pages which are lowly ranked
related to the topic at hand. The idea is to recursively execute an
exhaustive search up to a given depth ![]() , starting from the ``relatives'' of a highly
ranked page. Hence, a set of candidate pages is
obtained by retrieving pages reachable within a given
perimeter from a set of initial seeds. From the set of
candidate pages, we look for the page which has the best score
with respect to the topic at hand. This page and its
``relatives'' are inserted into the set of pages from which to
proceed the crawling process. Our assumption is that an
``ancestor'' with a good reference is likely to have other
useful references in its descendants further down the lineage
even if immediate scores of web pages closer to the ancestor
are low. We define a degree of relatedness
, starting from the ``relatives'' of a highly
ranked page. Hence, a set of candidate pages is
obtained by retrieving pages reachable within a given
perimeter from a set of initial seeds. From the set of
candidate pages, we look for the page which has the best score
with respect to the topic at hand. This page and its
``relatives'' are inserted into the set of pages from which to
proceed the crawling process. Our assumption is that an
``ancestor'' with a good reference is likely to have other
useful references in its descendants further down the lineage
even if immediate scores of web pages closer to the ancestor
are low. We define a degree of relatedness ![]() with respect to the page with
the best score. If
with respect to the page with
the best score. If ![]() is large, we
will include more distant ``cousins'' into the set of seeds
which are further and further away from the highest scored
page.
is large, we
will include more distant ``cousins'' into the set of seeds
which are further and further away from the highest scored
page.
This device overcomes the difficulties of using reinforcement learning in assigning credits, without the burden of solving a dynamic programming problem. These ideas may be considered as an extension to [1,2], as the use of a degree of relatedness extends the concept of child pages in [1] while avoiding the complex issue of inherence of scores, and the use of a perimeter is similar to the ``layer'' concept used in [2].
The web is a directed graph ![]() where
where ![]() is a node (i.e. a
page) and
is a node (i.e. a
page) and ![]() is a
directed link from node
is a
directed link from node ![]() to node
to node ![]() . The crawler, given
a seed node
. The crawler, given
a seed node ![]() , explores the web
, explores the web
![]() and builds the visit
tree
and builds the visit
tree ![]() , where
, where ![]() collects the visited
pages, and
collects the visited
pages, and
![]() . The border
. The border ![]() are the nodes in
are the nodes in
![]() that have outlinks to nodes outside
that have outlinks to nodes outside
![]() . The depth,
. The depth, ![]() , is the maximum distance from the seed node, and
the degree of relatedness
, is the maximum distance from the seed node, and
the degree of relatedness ![]() is defined as follows: an
is defined as follows: an ![]() ancestor of
ancestor of ![]() is a node
is a node ![]() for which there exists a path
for which there exists a path
![]() in
in ![]() with
with ![]() arcs to
arcs to
![]() such that
such that
![]() . Then, if
. Then, if
![]() , the
, the
![]() degree relatives of
degree relatives of
![]() are the nodes
are the nodes ![]() for which
for which
![]() holds. Finally,
the score of a page
holds. Finally,
the score of a page ![]() is the
relative importance of page
is the
relative importance of page ![]() about a
particular topic. Important pages are scored high.
about a
particular topic. Important pages are scored high.
Given ![]() and
and ![]() , the algorithm is as follows:
, the algorithm is as follows:
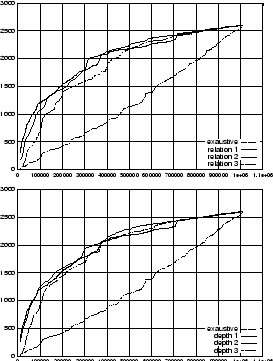
In order to validate our algorithm, we carried out some preliminary experiments. The purpose was to understand the behaviors of the algorithm and to clarify whether the method can be used to speedup a basic focused crawler (a crawler without sophisticated mechanisms for tunneling through lowly ranked pages). The data set we used was WT10G, distributed by CSIRO in Australia, that contains a snap shot of a portion of the world wide web consisting of 1,692,096 documents from 11,680 servers. We used a page classifier based on naive Bayes method [4] to assign a score to each page with respect to some randomly chosen topic.
The measures used to characterize the behaviour of the crawler
is the precision
![]() , where
, where
![]() is the number of relevant pages
that the crawler has visited, and
is the number of relevant pages
that the crawler has visited, and ![]() is the total number of pages visited. The experiment
illustrated in Figure 1 obtains
is the total number of pages visited. The experiment
illustrated in Figure 1 obtains
![]() as a function of
as a function of
![]() , and
, and ![]() respectively. Plotted is the number of web pages
visited against the number of relevant pages retrieved. The
topic used is ``Linux'' which has 2600 relevant pages in the
dataset.
respectively. Plotted is the number of web pages
visited against the number of relevant pages retrieved. The
topic used is ``Linux'' which has 2600 relevant pages in the
dataset.
|
Note that for ![]() our
crawler becomes a basic focused crawler. This experiment shows
that, at the beginning of the crawling, the basic focused
crawler is more efficient than our crawlers. But, as
our
crawler becomes a basic focused crawler. This experiment shows
that, at the beginning of the crawling, the basic focused
crawler is more efficient than our crawlers. But, as
![]() increases the crawlers with
increases the crawlers with
![]() give better
results. More precisely, Figure 1 shows
that choosing either
give better
results. More precisely, Figure 1 shows
that choosing either ![]() and/or
and/or ![]() produce the best results
in the later stage of the search process. This observation was
confirmed by other experiments (not shown due to lack of
space) on other general and special topics.
produce the best results
in the later stage of the search process. This observation was
confirmed by other experiments (not shown due to lack of
space) on other general and special topics.
The results have an interesting interpretation. The seeds, which
are on-topic pages, are probably directly connected to other
on-topic pages. Those pages can be easily collected at the
beginning by a basic focused crawler. Then, the crawling task
becomes more difficult making crawlers with ![]() and/or
and/or ![]() more
efficient. In the above example, pages addressing Linux are
often tightly linked to each other and hence, can be collected
quite easily. It is the retrieval of pages which are isolated
and difficult to find where the proposed algorithm gives
better results. However, the approach cannot tunnel
indefinitely as large values of
more
efficient. In the above example, pages addressing Linux are
often tightly linked to each other and hence, can be collected
quite easily. It is the retrieval of pages which are isolated
and difficult to find where the proposed algorithm gives
better results. However, the approach cannot tunnel
indefinitely as large values of ![]() and
and ![]() may force the retrieval of
more and more pages which are not immediately relevant to a
topic at hand.
may force the retrieval of
more and more pages which are not immediately relevant to a
topic at hand.
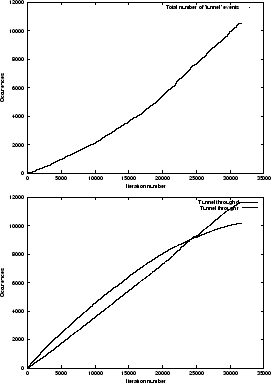
One of the main features of our proposed algorithm is its ability to tunnel through pages with a low score. An experiment has been conducted to give some indication on how this ability of the algorithm is employed. The upper graph in Figure 2
|
Finally, note that even if the presented results are preliminary and further experiments are needed to access its capabilities, and establish a direct comparison with other focused crawlers, the algorithm is considerably less computationally demanding than the ideas expressed in [1,2]. In addition, we do not require a large training set, and the training procedure is relatively simple.
This document was generated using the LaTeX2HTML translator Version 2002-2-1 (1.70)
The translation was initiated by Markus Hagenbuchner on
2003-03-28